Comments & Suggestions
For any inquiries or comments, please fill in the required information.
Loading...
Loading, please wait...
The Regulatory Sandboxes and Foresight Tools page highlights Saudi Arabia's innovative approach to fostering emerging technologies and future-proof policymaking. It showcases regulatory sandboxes that enable startups and businesses to test advanced digital solutions in controlled environments alongside foresight platforms like Estishraf, the International Performance Hub (IPH), and the GovTech Radar, which offer strategic insights to guide evidence-based decision-making and shape the future of digital governance in alignment with Vision 2030.
Share The Page
Regulatory sandboxes have become an important tool for accelerating the adoption of innovative technologies in Saudi Arabia. They provide a controlled environment where startups, SMEs, and established companies can test new digital solutions, products, and services under the supervision of relevant regulators. These initiatives align with the Kingdom's Vision 2030 objectives by fostering economic growth, encouraging investment, and enabling the development of emerging technology sectors.
Several government authorities have established regulatory sandboxes to address specific industries and technology applications:
The Saudi Central Bank (SAMA) has developed a Regulatory Sandbox focused on financial technologies (FinTech). This initiative welcomes local and international firms interested in testing new digital financial services in a live but controlled environment. The goal is to understand better the impact of these technologies on the Kingdom's financial sector while supporting the transformation of Saudi Arabia into a smart financial hub.
The Communications, Space and Technology Commission (CST) plays a leading role in advancing regulatory sandbox initiatives across sectors. CST operates multiple sandboxes, including:
The Digital Government Authority (DGA) has also launched a regulatory sandbox initiative tailored for government technology companies. Its objective is to explore and govern innovative digital platforms and services in the public sector, improve the regulatory environment for digital government services, and enhance the experience of beneficiaries by addressing regulatory challenges faced by companies and institutions operating in this space.
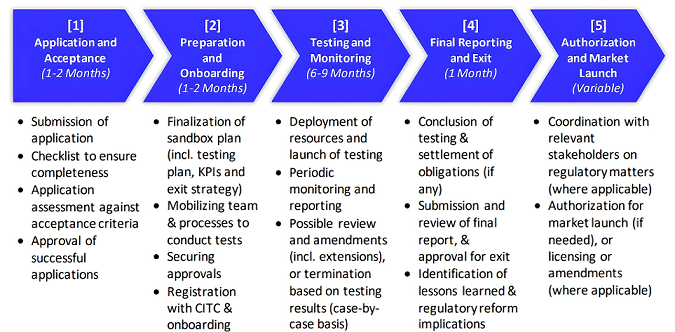
The sandboxes are open to companies introducing new digital business models or significantly enhancing existing use cases enabled by emerging technologies. However, participants must demonstrate readiness for commercial deployment and present clear, realistic testing plans. Business models lacking added value or maturity are not considered suitable for sandbox participation.
Several government agencies in Saudi Arabia have launched initiatives and platforms to explore emerging technologies' possibilities and limitations. These initiatives focus on understanding how such technologies could impact the future of digital government, the broader economy, and society at large.
One notable initiative is Estishraf, the analytical arm of the National Information Center (NIC). Estishraf supports decision-makers and government officials by harnessing the power of data science to enable evidence-based decision-making. It employs a highly skilled multidisciplinary team that applies advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to the vast centralized data in the National Data Bank. By doing so, Estishraf produces valuable business insights and domain-specific narratives that can inform policy and strategy.
Another significant platform is the International Performance Hub (IPH), developed by the National Center for Performance Measurement, known as 'Adaa.' The IPH is an interactive platform designed to track over 500 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across 12 primary pillars. These pillars cover critical sectors, including education, energy, social development, and industry. The platform aggregates and visualizes data from respected international sources such as the World Bank and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). What sets the IPH apart is its commitment to providing data that is:
In addition, the GovTech Radar plays a pivotal role in helping government entities accelerate the adoption of new technologies and innovative solutions that could shape the future of governance. This tool offers insights and research services designed to support government agencies in conducting future-scoping exercises and identifying promising technologies for potential use cases.
The GovTech Radar features a visualization tool that assesses 106 technologies using NASA's Technology Readiness Level (TRL) scale. This scale measures the level of technological maturity, ranging from 1 (the lowest stage of development) to 9 (fully developed and integrated into systems). The Radar serves as a benchmark to guide the integration of emerging technologies into digital governance initiatives.
To ensure alignment with global sustainability priorities, all technologies included in the GovTech Radar are analyzed in relation to the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Each technology is also categorized by taxonomy, including software, hardware, systems, materials, business models, and policies.
These technologies are clustered into seven affinity groups. Each group includes analytical essays highlighting the most significant technological impacts on key public sectors, such as:
By offering these tools and platforms, the Kingdom aims to enhance foresight capabilities, strengthen evidence-based policymaking, and promote the adoption of transformative technologies that align with its broader vision for digital transformation and sustainable development.