Comments & Suggestions
For any inquiries or comments, please fill in the required information.
Loading...
Loading, please wait...
The Digital Government Strategy outlines the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia's Vision and strategic direction for transforming government services through digital innovation. Rooted in the goals of Vision 2030 and aligned with international best practices, this strategy aims to deliver seamless, citizen-centric, and efficient digital services while fostering economic growth and sustainability. It serves as a guiding framework for national digital initiatives and underscores the Kingdom's commitment to leadership in digital governance.
Share The Page
Building on the foundation of the original Digital Government Strategy launched in 2023, this revised edition (2025–2030) reflects the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia's ongoing commitment to digital transformation. Significant progress has been achieved over the past two years, with most initial initiatives successfully implemented. These accomplishments have resulted in tangible improvements across government service delivery, operational efficiency, and user satisfaction.
The updated strategy integrates lessons from early implementation and aligns with emerging global trends, technologies, and policy shifts. It reinforces the Kingdom's ambition to remain at the forefront of digital governance by advancing citizen-centric, data-driven, and seamlessly connected services. While rooted in the foundational goals of Vision 2030, this revision introduces a renewed focus on agility, innovation, and sustainability as key drivers of the next phase of digital transformation.
The revised Digital Government Strategy (2025–2030) reaffirms and builds upon the Kingdom's core aspirations, including a commitment to sustainable development, service excellence, and global leadership in digital government. It defines the overarching Vision, mission, objectives, initiatives, and implementation roadmap to accelerate digital transformation in alignment with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Saudi Vision 2030.
By 2030, the government aims to provide fully integrated, seamless digital services that place citizens, residents, and businesses at the center of delivery. The ultimate aspiration is to position Saudi Arabia among the top 3 countries globally in digital government maturity. The anticipated cumulative impact by 2030 includes an estimated SAR 11.4 billion contribution to GDP and the creation of more than 26,000 new jobs. This transformation will be driven by continued innovation, policy agility, and collaborative efforts across government, the private sector, and civil society.
Based on the ambitions and aspirations of the Kingdom, the Vision of the strategy carries two key components that articulate Saudi Arabia's Digital Government ambitions as outlined in Vision 2030.

The mission embodies a purpose of how the digital government is looking to accomplish its Vision:

The Strategy defines four six strategic pillars to achieve the Kingdom's aspirations and Vision.
The six strategic pillars include:
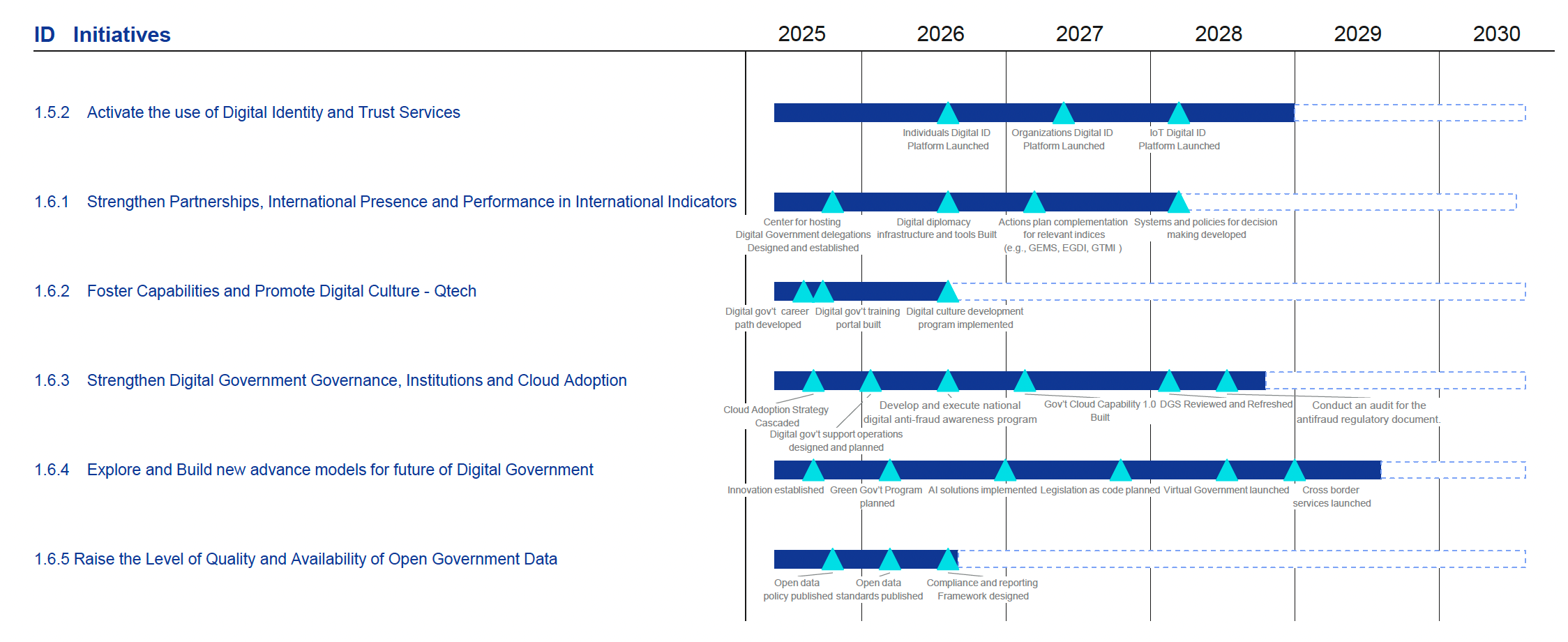
The Strategy outlines 17 strategic initiatives designed to achieve the Vision and objectives of the Digital Government Strategy.
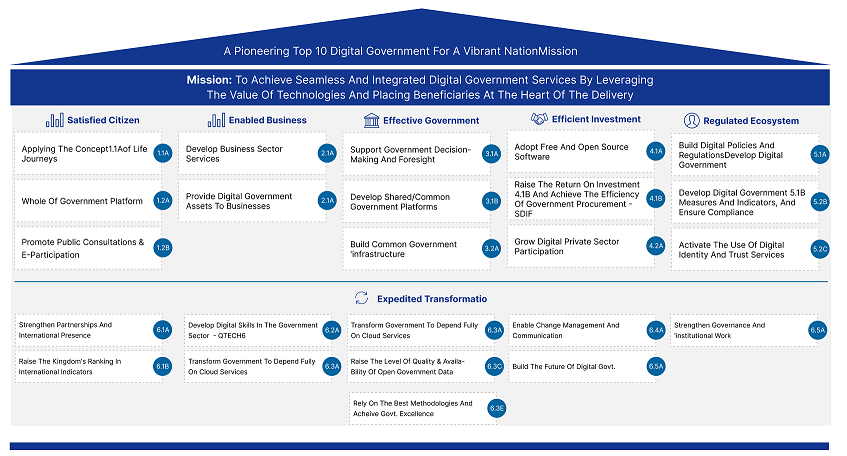
The initiatives are categorized based on their impact and implementation priority: seven are considered game-changers, four are foundational prerequisites, and six are identified as quick wins.
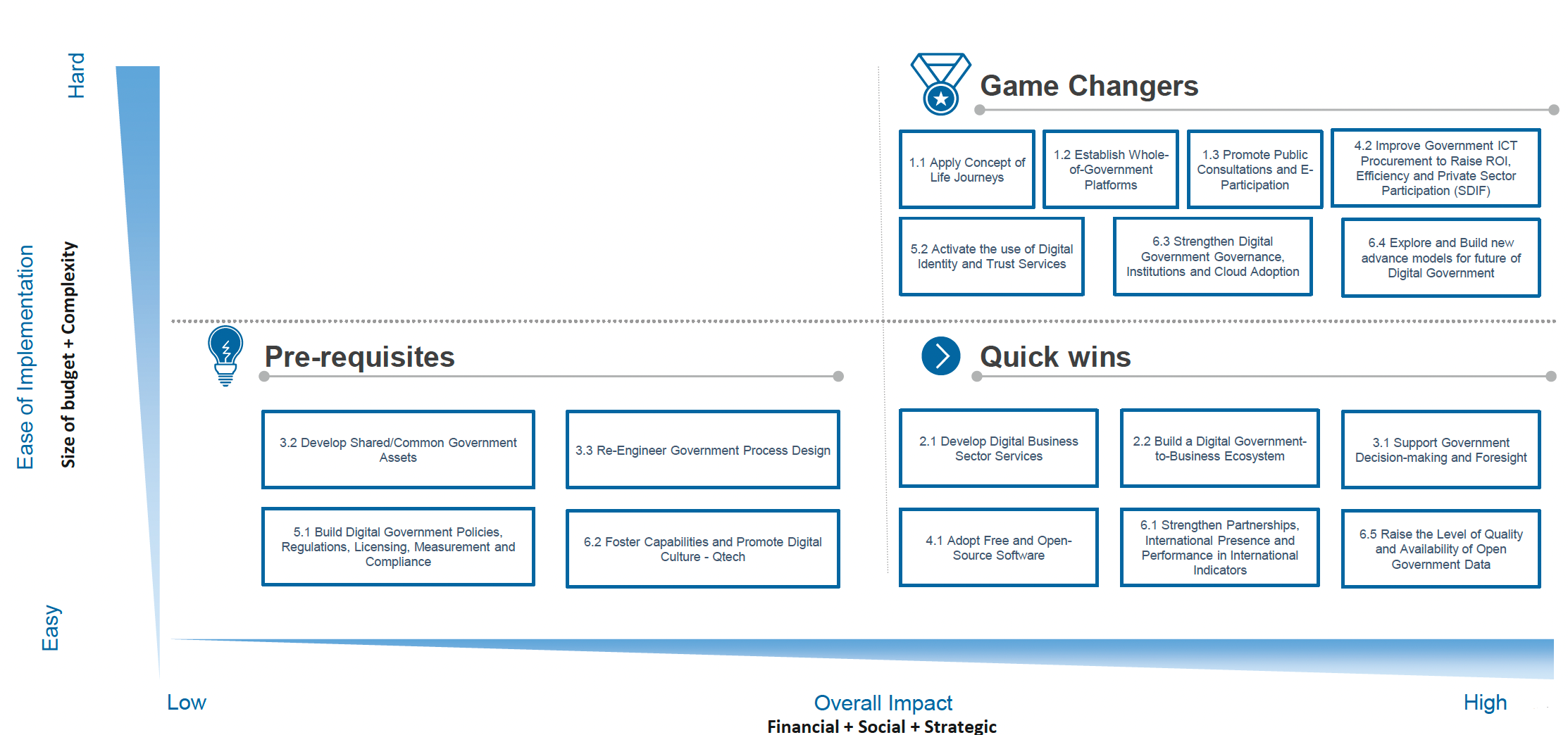
To enable effective monitoring and evaluation, the Strategy includes 14 strategic Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that provide a comprehensive view of implementation progress.
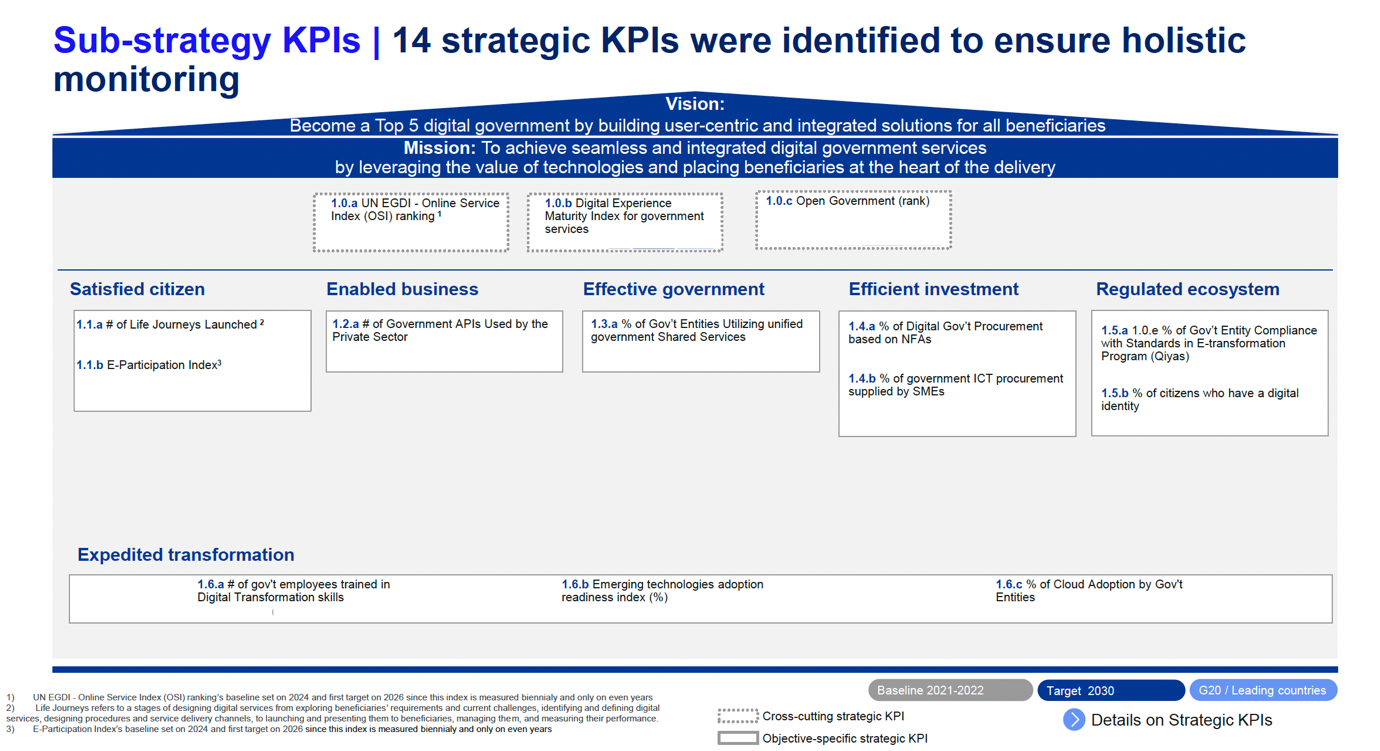
The Strategy is supported by a detailed roadmap that outlines program initiation, execution phases, key milestones, and ongoing operations and support mechanisms.
Digital Government Strategy will contribute to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and have a social impact on multiple groups of citizens. It will contribute to achieving the SDGs 3, 4, 8, 9, 11, 13, 16, and 17. Numerous citizens will benefit from implementing the strategy's objectives and programs, such as citizens, residents, families, vulnerable groups, women, students, patients, tourists, visitors, businesses, investors, etc.

The strategy is guided and aligned with the Vision 2030 goals and strategic objectives. The strategy specifies how KSA will deliver on its Vision of digitally transforming the government and building world-class smart government capabilities. It contributes to achieving the following Vision 2030 objectives:
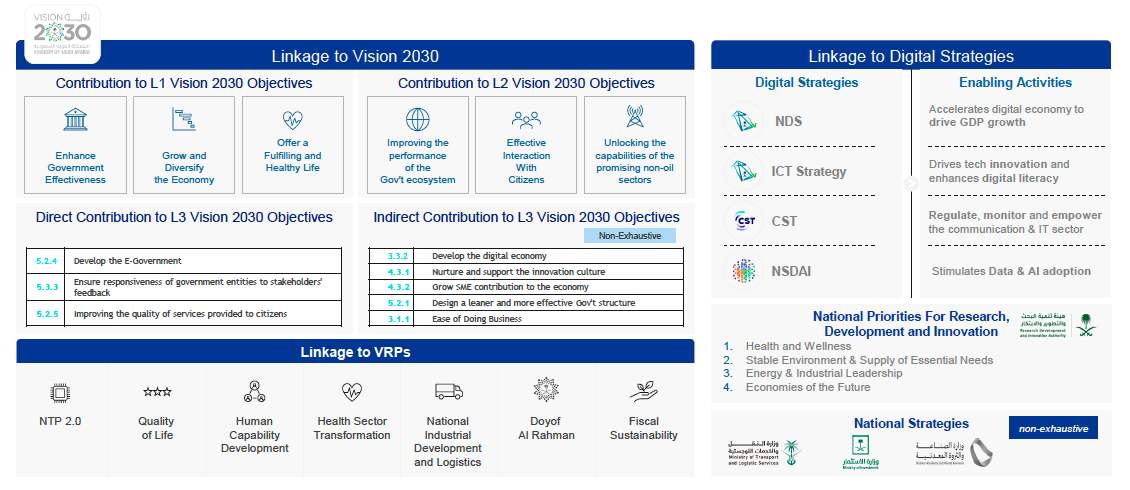
The Digital Government Strategy is also critical to the success of several Vision Realization Programs (VRPs), such as the National Transformation Program, Quality of Life Program, Human Capability Development Program, Health Sector Transformation Program, National Industrial Development and Logistics Program, Doyof Al Rahman Program, and Fiscal Sustainability Program. The demands from the VRPs (over 170 initiatives are linked with Digital Government) are extensive. The need to improve government services, provide shared platforms, develop standards and regulations, and improve decision-making is among the key needs. All VRPs are aimed at operationalizing Vision 2030 strategic objectives.
The Digital Government Strategy is also fully aligned with the other key ICT sector strategies, such as the ICT Sector Strategy, National Strategy for Data & AI, Cyber Security Strategy, etc.
The Digital Government Strategy was also developed following the guidelines published by UNDESA on the Open Government Data for Citizen Engagement and the OECD Recommendation on Digital Government Strategies. The Strategy addresses 12 OECD recommendations:
In addition, the government is working continuously with multilateral agencies and governments worldwide for guidelines and strategy alignment on eGovernment through global partnerships like G20, GCC, and other multilateral and bilateral participation.
The eParticipation and Digital Inclusion are among the most significant priorities identified in Vision 2030 and the Digital Government Strategy.
To strengthen e-participation, the Strategy includes the Strategic pillar of Satisfied citizen: Personalize digital services to Saudi citizens, residents, and visitors through life moments. This objective focuses on increasing citizen involvement by placing them at the center of government and engaging them in service design and policy-making processes. To support this objective, the Strategy outlines Initiative 1.1.3 Promote Public Consultations & E-Participation, encouraging citizens to shape government decisions and services actively.
To advance Digital Inclusion, the Strategy defines additional strategic pillar, such as Strategic pillar Expedited transformation 1.6 Accelerate the digital transformation of KSA by working closely with the Government Entities and provide national leadership and guidance in innovation, cloud computing, open source, enterprise architecture, and the future of digital government. The Strategy outlines Initiative 1.6.2 Foster Capabilities and Promote Digital Culture (Q-tech) to support this objective.
The Digital Government Policy also sets the overall direction for sustainable, long-term digital government transformation in the Kingdom. The Policy's first pillar, Engagement, emphasizes the participation and collaboration of government institutions, the private sector, civil society, and beneficiaries. It encourages these stakeholders to provide valuable input for digital government implementation. The Engagement Pillar comprises six principles: Transparency, Collaboration, Data Privacy, Information Sharing, Innovative Government Culture, and Inclusion.
In addition, the inclusion-by-default approach is embedded in the Digital Government Regulatory Framework, which outlines eight principles, including the second principle: Open-by-default. This principle aims to make government data and policy-making processes (including algorithms) accessible for public engagement within the boundaries of existing legislation and national interests, thereby promoting transparency, accountability, and inclusion.
Finally, the Digital Government Authority has adopted a document entitled "Electronic Participation Controls," which aims to enhance community participation in the Kingdom. These controls contribute to raising the level of participation and interaction between government agencies and beneficiaries and providing a smooth experience for beneficiaries of digital government services, which will enhance the empowerment of beneficiaries to participate in building and supporting the decisions of government agencies to strengthen community participation.
This document also reinforces this trend and is based on the stages of e-participation, which are designed based on best practices that identify the main elements of effective design and strategic implementation in order to achieve higher levels of interaction and participation at the level of the Kingdom. The main objective of these controls is to contribute to improving the performance of the government apparatus and enabling social responsibility through interaction with beneficiaries, and this, in turn, will contribute to increasing transparency in all government sectors, enhancing communication with beneficiaries, including individuals and companies, as well as the response of government agencies to the opinions of various stakeholders.
For more information, click here.
The issue of national data governance is high on the strategy objectives. Three strategic pillars and objectives are particularly relevant:
To support these objectives, the Strategy outlines several initiatives, including:
Collectively, these must comply with national Cybersecurity legislation, Data and Privacy protection legislation, and National Standards for Interoperability.
Saudi Arabia has implemented a National Digital Identity Management System since 2008. All Saudi citizens and residents can create their digital identity (or electronic ID) by registering on the National Single Sign-On platform developed by the National Information Center. This digital ID enables access to over 2,000 government online services through the my.gov.sa portal and services provided by other government entities and third parties, including banks and telecom providers.
The Digital Government Strategy strengthens this commitment through Strategic pillar 1.5 Regulated ecosystem: Build a universal digital ID & trust ecosystem used by Saudi citizens, and a future-proof harmonized, and adaptive digital regulatory regime, which aims to achieve universal uptake of a trusted national digital identity in Saudi Arabia. To operationalize this objective, the Strategy introduces Initiative 1.5.2 Activate the use of Digital Identity and Trust Services, focused on the use of digital identity and trust services to ensure secure, efficient, and user-friendly access to government and private sector services.
For more information, click here.
The Digital Government Strategy explicitly incorporates the digital-by-design principle. This is reflected in Strategic pillar 1.1 Satisfied citizen: Personalize digital services to Saudi citizens, residents, and visitors through life moments, which aims to ensure Saudi citizens' satisfaction with the use of digital services, embedding digital-by-design as a core concept. The Strategy outlines Initiatives 1.1.1 Apply Concept of Life Journeys and 1.1.2 Establish Whole-of-Government Platforms to support its implementation, which promotes integrated and user-centric digital services.
Digital by design is regulated and defined in the Digital Government Regulatory Framework, which includes eight principles, the first of which is Digital by design. The objective is to establish clear organizational leadership, paired with effective coordination and enforcement mechanisms where "digital" is considered a technical topic and a mandatory transformative element to be embedded throughout policy processes.
The Digital Government Policy also sets the overall direction for achieving sustainable long-term government digital transformation in the Kingdom. The policy's second pillar (component) is dedicated to transformation, which includes the enablers that drive government development, with the main emphasis being modernization, not technology.
The Once-Only principle is recognized as one of the essential elements of the Digital Government Strategy. It is an eGovernment principle that aims to ensure that citizens and businesses only have to provide certain information to the government authorities only once (also known as a "Tell us Once Principle").
The principle is embedded within Strategic pillar 1.1 Satisfied citizen: Personalize digital services to Saudi citizens, residents, and visitors through life moments, and is operationalized through Initiatives 1.1.1 Apply Concept of Life Journeys and 1.1.2 Establish Whole-of-Government Platforms, which promotes data sharing and integration across government entities.
The once-only principle is regulated and defined in the Digital Government Regulatory Framework, which includes eight principles, out of which the eighth is Once only Principle. The objective is to ensure that citizens, institutions, and companies only have to provide certain standard information to the authorities and administrations once.
Compliance with national Cybersecurity legislation, Data and Privacy protection legislation, and National Standards for Interoperability underpin the implementation of the Once-Only principle.
The Digital Government Strategy directly references the life cycle (life events) approach as one of the main preconditions for increasing the citizens' satisfaction. Strategic pillar 1.1 Satisfied citizen: Personalize digital services to Saudi citizens, residents, and visitors through life moments. This approach incorporates Initiatives 1.1.1 Apply Concept of Life Journeys and 1.1.2 Establish Whole-of-Government Platforms formally included as part of the Strategy's implementation plan.
The life-cycle approach is also regulated and defined in the Digital Government Regulatory Framework, which includes eight principles. The fourth is the Government as a Platform, which obliges government entities to act as a platform for meeting users' needs. It also provides clear and transparent sources of guidelines, tools, data, and software that equip teams to deliver user-driven, consistent, seamless, integrated, proactive, cross-sectoral service delivery.
Saudi Arabia's Digital Government Strategy and National Strategy for Data & AI provide a clear roadmap for leveraging AI and emerging technologies to improve public service delivery and digital transformation. These strategies reinforce the Kingdom's commitment to AI-driven governance, policy innovation, and sustainable digital development.
The Digital Government Strategy provides a structured framework for modernizing public services, improving governance efficiency, and driving digital transformation. It defines six strategic pillars and 17 initiatives, focusing on emerging technologies. One of the strategic objectives directly addresses the use of AI and emerging technologies:
Expedited Transformation: 1.6 Accelerate the digital transformation of KSA by working closely with the Government Entities and provide national leadership and guidance in innovation, cloud computing, open source, enterprise architecture, and the future of digital government.
This strategy aligns with Vision 2030, ensuring that AI and digital transformation play a key role in delivering efficient, high-quality public services.
In addition, the National Strategy for Data & AI outlines a roadmap for harnessing AI to transform public services and key economic sectors. It focuses on six dimensions:
Key Dimensions and Objectives
Five priority sectors have been identified for AI adoption to leverage AI for enhanced service delivery and innovation., including:
Both strategies aim to enhance government efficiency, improve public services, and accelerate digital transformation by leveraging emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI).